As we enter the 21st century, the global wave of digitalization and intelligence has swept across the globe, with optical silicone and optical silicones now fully integrated into various fields such as daily life, industry, transportation, and healthcare. From smartphones, high-definition cameras, and smart display devices to automotive lighting, 5G communication, and virtual reality, various end-user devices are placing increasingly higher demands on materials in terms of optical properties, reliability, miniaturization, and durability. What are the applications of optical silicone?
As a new generation of high-end silicone-based functional materials, spherical silicone resins—a typical optical silicone—with their unique spatial structure, controllable surface properties, and excellent physical performance, are leading the development trend of microstructural materials and functional packaging in the optical electronics industry. Additionally, due to their uniform spherical structure distribution, excellent material flowability (including low viscosity as in optical liquid silicone rubber), and strong dimensional stability, they are suitable for various processing techniques such as injection molding of complex shapes. The low viscosity and processability of optical silicone make it possible to create complex shapes more easily than with traditional materials like glass or organic polymers. The importance of the mold in these processing techniques is crucial, as proper mold design and material interaction ensure high surface quality and dimensional stability in optical silicone components. They exhibit extremely high insulation performance, strong interface compatibility, and ease of use with multiple substrates, while also offering excellent functional expandability, enabling customized requirements through surface modification. In the manufacturing process, these properties make silicone rubber and optical silicones ideal for producing flexible, optically clear, and complex components. In terms of environmental protection, this material complies with environmental regulations such as RoHS and REACH, contains no harmful substances like plasticizers, and is safe and reliable. Therefore, silicone spherical silicone resin outperforms traditional filler materials in terms of high performance, environmental friendliness, and process adaptability, offering broad application prospects—especially for optical applications, medical applications, and lighting applications.
There are eight aspects to introducing optical silicone:
- What issues do untreated light sources commonly face?
- What are the user requirements in the optical industry?
- What is the principle of light-diffusing materials?
- What are the common types of light-diffusing agents?
- What are the physical properties of spherical silicone resin?
- What are the advantages of silicone resin in optical applications?
- What are silicone optical applications?
1. What issues do untreated light sources commonly face?
(1) Light concentration — Light is concentrated and not soft, causing visual discomfort.
(2) Severe glare — Exposed light sources such as LED chips emit glaring point-like light, easily causing visual fatigue.
(3) Uneven brightness — In LCD backlights, untreated areas may exhibit noticeable light spots and dark zones.
To address these issues, light-diffusing materials such as optical silicone and optically clear silicones are required to convert point light sources into line or area light sources, achieving uniform light intensity distribution through beam shaping to enhance lighting quality and reduce glare.

2. What are the user requirements in the optical industry?
(1) Higher optical transparency and precision molding: extremely high requirements for transmittance and purity; for example, optically clear silicone offers high transparency and is increasingly favored in optical applications where optically clear silicones or optical liquid silicone rubber are specified.
(2) Excellent heat resistance and aging performance: no discoloration or deformation under long-term high-temperature, ultraviolet exposure, high humidity, and strong light conditions; opt for UV resistance to avoid losing transparency.
(3) Extremely low thermal expansion coefficient and deformation: to ensure dimensional stability and prevent device structural failure due to temperature changes, a key factor in designing parts with complex shapes or fine features.
(4) Ultimate micro/nano processing capability and interface compatibility: Adapt to complex chip structures, micro-lens arrays, thicker walls, small undercuts, and ultra-thin optical layers, which are possible thanks to injection molding and suitable material characteristics.
(5) High refractive index and uniformity: Enhance display and optical efficiency, especially for lenses, lighting, and light pipes.
(6) Traditional organic fillers, powders, and resins suffer from poor weather resistance, yellowing, leaching contamination, and processing difficulties. In contrast, structurally regular, high-temperature-resistant, optically clear silicone (optical liquid silicone rubber) and optical-grade silicone rubber have emerged, providing the industry with a new material solution.

3. What is the principle of light-diffusing materials?
The balance between “transmittance” and “haze” is the key performance characteristic of light-diffusing materials. This is typically achieved by adding light-diffusing agents to transparent polymer matrices (such as PS, PC, PMMA/polymethyl methacrylate, or polycarbonate). The core principle is that differences in refractive index cause light rays to deflect in their propagation direction, thereby achieving diffusion. Optical silicone or liquid silicone rubber can enhance this effect due to their tailored optical properties.
4. What are the common types of light-diffusing agents?
(1) Inorganic types (example: silica, titanium dioxide)
Advantages: High refractive index, strong diffusion capability
Disadvantages: Uneven particle size, low light transmittance, irregular particle shape
(2) Organic (example: acrylic resin microspheres, polystyrene microspheres)
Advantages: High light transmittance, good dispersibility
Disadvantages: Poor heat resistance, prone to deformation during processing or use
(3) Advantages of spherical silicone resin/optical silicone: Combining strengths and weaknesses, it offers both diffusion and stability
Excellent light diffusion properties
High sphericity and smooth surface, reducing light loss caused by irregular shapes
Moderate refractive index (~1.43), usable in PS or polycarbonate for the same haze with less material
Narrow particle size distribution, consistent size, resulting in uniform light scattering
Excellent thermal stability, resistant to heat, even during extreme exposure
Wide operating temperature range supporting high uv resistance/heat resistance, up to 400°C, preventing material deformation in LEDs and other optical applications.
Significantly lighter than glass and some plastics/alternatives, and with the flexibility to produce complex shapes more easily (including negative draft and undercuts that are difficult for other manufacturing methods or materials).

5. What are the physical properties of spherical silicone resin?
Silicone spherical silicone resin, a type of optical silicone, primarily consists of highly cross-linked, regularly ordered [(CH₃SiO₁.₅)ₙ] structural units that self-assemble into spherical particles ranging from nanometers to micrometers in size. Typical particle sizes can be controlled between 0.2 and 5 μm, with a smooth surface, a narrow particle size distribution, and outstanding mechanical and chemical stability.
The backbone consists of Si-O-Si bonds, giving excellent heat resistance and UV resistance, far exceeding that of conventional plastics and polymers.
The spherical morphology confers excellent light scattering, uniform filling, and interface compatibility.
The highly crosslinked structure ensures superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability—critical in molding and assembly for optical components that need to resist internal stresses.
Functional groups (e.g., methyl, phenyl, vinyl, hydrogen-containing groups, etc.) can be introduced onto the surface as required for contact with other materials, enhancing synergistic interaction with the substrate.
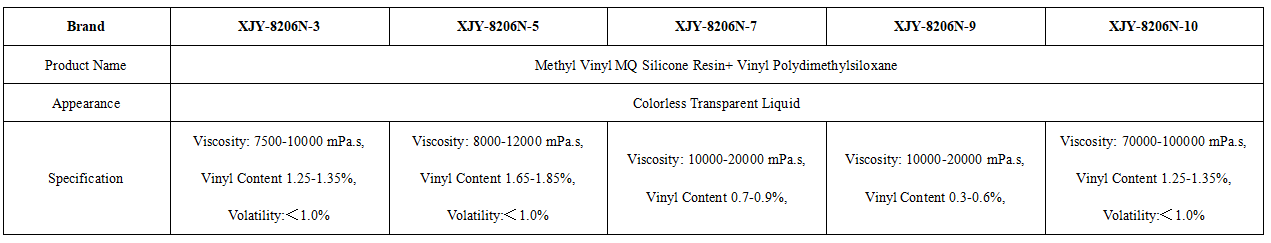
XJY-8206 Methyl Vinyl Siloxane Resin
It is made from the polymerization of tetrafunctional siloxane (Q) and monofunctional methyl siloxane (M). Silicone polymers and silicone compounds made from VMQ materials provide a wide range of temperatures, abrasion resistance, weathering, compression coagulation resistance, resistance to ultraviolet radiation, and other physical properties, and can be used in electronic and electrical appliances, LED, and other industries.
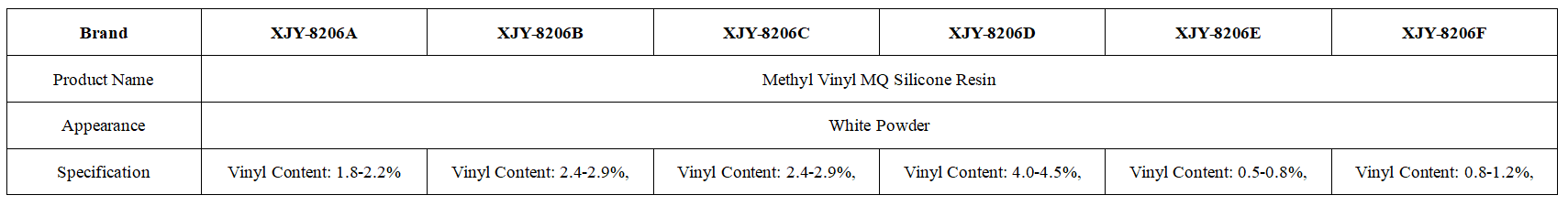
XJY-8206N Series Solution Methyl Vinyl MQ Silicone Resin
It is colorless and transparent and is composed of vinyl MQ silicone resin and vinyl silicone oil. It can be used for LSR(optical liquid silicone rubber), liquid additive silicone rubber, and can also be used for other two-component additive adhesives.
6. What are the advantages of silicone resin in optical applications?
(1) Optimized optical performance, enabling high-end display and lighting
The spherical structure of organosilicon (including optical silicone/optically clear silicone) outperforms non-spherical powders due to its uniform scattering, low light loss, and optimized refractive index and Abbe number. This allows for high light transmission, reflection control, and optical clarity, making it ideal for lenses, lighting, and light pipes. In LED applications or optical applications demanding high brightness, the use of optically clear silicone ensures thicker walls do not cause light yellowing or loss of transparency, unlike some plastics/polycarbonate options. Additionally, the application of optical liquid silicone rubber in LED and photonics devices reduces energy consumption, extends product lifespan, and improves overall efficiency in lighting systems.
(2) Excellent Heat Resistance/UV Resistance and Aging Resistance
The Si-O backbone’s superior heat/UV resistance ensures material stability in high-power LED, medical applications, and lighting applications. Optical silicone does not lose transparency after prolonged exposure to UV or heat, providing enhanced device reliability for demanding environments.
(3) Precise size control and compatibility with micro-nano processes
Spherical silicone resin allows precise molding/manufacturing of complex shapes, fine features, and small undercuts—even in injection molding/molded applications with negative draft—thanks to its low viscosity, flexibility, and surface flow properties. This results in greater design freedom, reducing costs and enabling complex shapes to be easier than with glass or other plastics. Designers can achieve optimal function with reduced likelihood of defects due to internal stresses.
(4) Strong interface control capability, extending device lifespan
Optical silicones/optical silicone rubber serve as key functional layer materials, substantially improving seal integrity and contact strength in lenses, light guides, and medical applications. Their stable bonding reduces assembly failures and supports the manufacturing of robust, long-lasting optical devices.
(5) Environmentally friendly, meeting high-level safety and sustainability requirements
Optically clear silicones and optical liquid silicone rubber are solvent-free, have low VOCs, and produce non-toxic decomposition products under heat, with no heavy metal content—meeting medical and lighting safety standards (including Dow Corning and other major brands).
7 . What are silicone optical applications?
(1) Optical-Grade LED Encapsulation
With the advancement of LED applications (requiring high light transmission, precise molding, and dimensional stability), optical silicone (optically clear silicone, optical liquid silicone rubber) is used as encapsulation or diffusion material. This enhances luminous flux, light output uniformity, and resistance to heat/uv, ensuring longer device lifespan and reducing maintenance—a clear benefit over glass/polycarbonate/plastics.
Application Value
Enhances color rendering and transparency for blue/white LEDs
Improves encapsulation density, moisture resistance, and extends operational range
Supports injection molding, precision manufacturing, and complex molded geometries
(2) Electronic Displays and Touchscreen Modules
For lighting, displays, and touchscreen modules (OLED, Mini-LED/LCD), optical silicone and optically clear silicone provide excellent optical properties (high transparency, low reflection, high Abbe number) and durability, especially in curved or ultra-thin designs where dimensional stability, anti-static, and chemical resistance are paramount.
Application Value
Achieves smooth imaging even on ultra-large, ultra-thin displays
Withstands high-frequency wear and maintains uniformity even with extensive patient use in medical applications
(3) Camera and Optical Lens Encapsulation
Optical silicone/liquid silicone rubber/optically clear silicone is used as lens axis filler/support and as an anti-soiling, anti-reflective nano-coating, improving lens imaging clarity, long-term transparency, and surface durability.
Application Value
Enhances mechanical stability and reduces deformation
Maintains optical performance even with significant exposure to heat, uv, and internal stresses
(4) Optical Communication and IoT Components
In 5G/6G, optical silicone with very low viscosity and low levels of impurities enables precise manufacturing of optical components, reducing optical loss and supporting innovations in photonic circuits.
Application Value
Reducing costs by enabling lightweight, significantly lighter assemblies
Supporting efficient, compact, high-quality light guides
(5) Emerging Smart Wearables and Automotive Optical Components
Smartwatches, AR glasses, and autonomous driving cameras—all increasingly depend on optically clear silicone, optical liquid silicone rubber, and optical silicones for wear-resistance, high clarity, a wide operating temperature range, and flexibility in designing parts and assembly.
Application Value
Maintains long-term clarity and transparency after heavy use
Enables complex shapes and robust seals in variable environments

8. How can the performance of silicone optical materials be improved?
Compared to traditional inorganic or organic fillers, optical silicone/optical liquid silicone rubber/optically clear silicone offers superior optical properties, heat/UV resistance, and dimensional stability, and allows for innovative manufacturing processes and design challenges. Optimizing cure chemistry and molding cycles, fine features, and complex shapes offers design freedom and stability for applications from light pipes/light guides to advanced medical and lighting devices. Selecting the appropriate material—such as optically clear silicones—can solve design challenges, improve function, and support high-level patient safety in medical applications(make patients comfortable).
XJY Silicone is one of China's leading manufacturers of organic silicon MQ resins and VMQ organic silicones, with over 30 years of R&D and manufacturing experience in the organic silicon industry, holding more than 15 related patents and technical support. Our organic silicon raw material products meet the needs of the optical silicone, liquid silicone rubber, manufacturing, and medical applications markets and provide diversified customized solutions for qualified industrial users.
![]()