The semiconductor industry is the cornerstone of modern manufacturing, supporting nearly all contemporary high-tech industries such as information technology, intelligent systems, electric vehicles, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence. In the fields of semiconductor manufacturing and packaging, reliable, high-performance bonding, packaging, and protective materials are of critical importance. As chip design continues to evolve toward miniaturization, high integration, and extreme environment adaptability, adhesive materials used in processes such as chip protection, temporary fixation, and transfer are also subject to increasingly stringent performance standards. How are silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives used in the semiconductor industry?
As a specialized adhesive material, silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives, with their unique molecular structure and physical-chemical properties, are increasingly widely used in semiconductor packaging, testing, temporary bonding, lithography processes, and high-end electronic assembly. This article will provide a detailed explanation of the core value of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives in the semiconductor industry, aiding relevant enterprises or R&D teams in making informed decisions.
There are six aspects to introducing silicone PSA:
- What is the definition of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive?
- What are the requirements for the silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive?
- What are the applications of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives?
- What are the advantages of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives?
- What are the market trends of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive?
- How to choose a silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive?
1. What is the definition of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive?
Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive is a type of polymer material based on a polysiloxane backbone (i.e., Si-O-Si bonds) combined with appropriate organic functional groups (such as methyl, phenyl, vinyl, etc.). This type of adhesive does not require heating or solvent evaporation; it can be instantly bonded and peeled off with light pressure, forming a robust fixed state while also facilitating subsequent peeling and repositioning.
The unique structural design of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives enables them to exhibit adhesion and resistance far surpassing that of traditional acrylic, rubber, and other conventional pressure-sensitive adhesives under extreme temperatures, humidity, chemical resistance, or high cleanliness requirements. They can be formulated for low tack or strong adhesion, depending on semiconductor substrates and processes.
Since the development of silicone resins in the 1960s, their applications have expanded from general industrial bonding to advanced manufacturing fields such as aerospace, electronics, automotive, healthcare, and semiconductors. Compared to acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesives (Acrylic PSA) and rubber-based PSA, the development of silicone psa relies more on high-purity silicone monomers, precise molecular weight control technology, advanced polymerization and blending equipment, as well as a deep understanding of downstream harsh environments and a wide array of extreme application requirements.

2. What are the requirements for the silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive?
With the advancement of Moore's Law, chip integration continues to increase, making micron- and nanometer-level packaging technologies increasingly mainstream. New processes such as high-density packaging (HDP), system-in-package (SiP), flip chip, and wafer-level packaging (WLP) are gradually becoming widespread. Meanwhile, semiconductor applications are expanding from IT, communications, and consumer electronics into high-reliability fields such as aerospace, automotive electronics, high-speed computing, big data, 5G/6G RF, and defense.
(1) Extremely low metal/inorganic impurity background to prevent ion migration and contamination
(2) High purity and low outgassing to avoid residue volatilization during extreme temperatures and high-temperature processes
(3) Wide operating temperature range, with high and low temperature resistance (-55°C to 300°C)
(4) High insulation and stability, preventing short circuits or current leakage
(5) Controllable peelability and re-adhesion (peel adhesion), facilitating temporary chip fixation and process transfer
(6) Compliance with environmental and safety regulations such as RoHS and REACH
XJY-301 Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives
It is made from the specific structure of silicone resin and high molecular weight polydimethylsiloxane in cooperation with organic adhesive, which is suitable for specific scene conditions.
Compared with natural rubber, it is characterized by heat resistance, high stability, good electric insulation, good transparency, high peel adhesion, and chemical resistance etc. It has a wide range of applications in industrial product processing, electronic processing, optical materials, health care, and mica tapes, splicing tapes, protective films, and other fields.
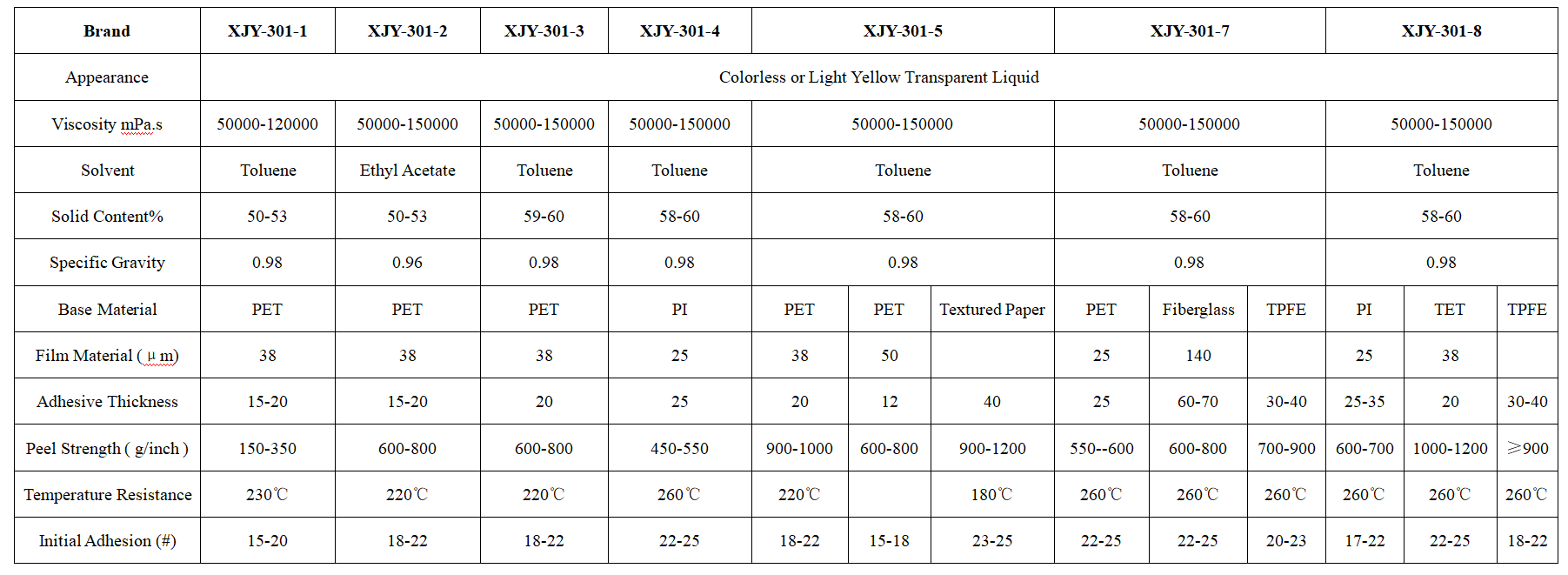
3. What are the applications of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives?
Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives provide the following critical services to the semiconductor industry:
(1)Temporary bonding and bonding during wafer processing
During high-intensity processing steps such as wafer thinning, grinding, etching, and chemical mechanical polishing (CMP), fragile wafers require temporary fixation or bonding. At this stage, silicone PSA, with its high cleanliness, high-temperature resistance, low residue, and easy peelability, is widely used as temporary bonding tape (Tape for Temporary Bonding) to ensure the wafer remains intact and stable during back-side processing. The adhesive is frequently coated onto films to form precise protective films that shield wafers from moisture and debris.
(2)Protection and Temporary Fixation in Chip Packaging
During the packaging of integrated circuits such as CPUs, GPUs, and memory chips (including traditional DIP, SOP, QFN, BGA, FC, and other series), it is often necessary to attach bare dies or unpackaged chips in a specific orientation to carrier substrates, test wafers, or transfer disks before performing operations such as soldering, dispensing, curing, and testing. Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives, with their controllable initial tack and re-adhesion properties, serve as reliable protective films and temporary fixation adhesives.

(3)Precision Lithography Process Applications
In critical stages such as advanced lithography and micro/nano imprinting, silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives can be fabricated into mask protection films, temporary masking tapes, or support substrates for nano-transfer printing, effectively ensuring operational safety under conditions requiring extremely small dimensions and absolute cleanliness.
(4)Protection in Chip Testing, Sorting, and Cutting Processes
During processes such as dicing, sorting, and visual inspection, silicone pressure-sensitive films are used to protect the surfaces of precision chips and MEMS devices. Commonly used films serve as temporary backing adhesives to prevent scratches, debris splashes, and contamination. Their excellent chemical resistance keeps delicate substrates safe even in harsh environments.
(5)Adhesion and Re-positioning of Flexible Circuits and Micro-Components During Assembly
During assembly, adjustment, and pre-alignment of FPC (flexible circuits) and high-density packaging module components, pressure-sensitive adhesives are used to achieve precise positioning and temporary bonding, facilitating subsequent steps such as welding, surface mounting, and curing.
4. What are the advantages of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives?
Compared to traditional PSAs, silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives exhibit unparalleled key performance characteristics in semiconductor processes:
(1)Exceptional high-temperature and low-temperature performance
The Si-O-Si backbone of silicone grants the material an extremely wide operating temperature range (-55°C to 300°C or higher), maintaining stable initial adhesion and holding power under harsh conditions such as chip thinning, LED high-temperature baking, IC packaging molding, and laser etching. Such properties also make silicone PSAs suitable for aerospace and automotive applications that require robust reliability under extreme temperatures.

(2)Very low chemical residue and outgassing
High-purity silicone psa releases virtually no organic/inorganic impurities during peeling or heating, outperforming acrylic and other polymers. This eliminates the risk of introducing non-target metal ions or residue contamination on the packaging surface, thereby improving yield rates.
(3)High electrical insulation and dielectric stability
For high-frequency components, RF chips, and millimeter-wave devices, the high insulation and low dielectric loss (low Dk and Df values) of silicones can significantly suppress parasitic currents, enhancing the safety of communication and integrated circuit operations.
(4)High Flexibility and Stress-Relief Capability
Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives possess rubber and elastomer characteristics—for example, their similarity to silicone rubber—capable of cushioning mechanical shocks and thermal expansion impacts during chip thinning and cutting processes, effectively reducing the risk of chip damage.
(5)Excellent processability and peelability
Peel force can be customized according to process requirements (from several tens of grams to over kilograms per 25 mm), ensuring clean, residue-free, and bubble-free peeling. It supports fully automated roll-to-roll, sheet-to-sheet, slitting, and lamination processes (line manufacturing), significantly improving automated production efficiency. A primer can also be used to enhance bonding to difficult substrates.
(6)High cleanliness, anti-static, and dust-proof properties
The silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive system does not easily adsorb dust and can be formulated to achieve anti-static properties, effectively preventing ESD damage and the adsorption of nano-sized impurities, ensuring compliance with cleanroom application requirements.
(7)Compliant with environmental regulations and ultra-low VOC
It meets international environmental regulations such as RoHS, REACH, and lead-free directives, supporting green semiconductor manufacturing and reducing environmental impact.
5. What are the market trends of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive?
(1) Global Semiconductor Adhesive Materials Market
According to industry consulting data from Yole, TechNavio, and IC Insights, the global market for semiconductor packaging adhesives exceeded 2.5 billion USD in 2023, with high-end pressure-sensitive adhesive materials growing at an annual rate exceeding 20%, and is expected to continue expanding in precision manufacturing, optoelectronics, medical devices, and sensing fields.
(2) Major Application Countries and Markets
China, South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan: Global leaders in semiconductor manufacturing, with strong demand for temporary bonding and MEMS processing, requiring an extremely stable supply of source materials.
United States, Germany, and Singapore: IDM giants and wafer foundries are continuously expanding high-end chip production capacity, leading to significant procurement of anti-contamination, high-temperature, low-residue pressure-sensitive adhesive products, labels, and advanced films.
Emerging markets such as India and Southeast Asia: Rapid migration of semiconductor back-end packaging processes, with growing demand for cost-effective PSA materials with good process compatibility and additive system flexibility.
(3) Technological and Product Development Trends
Upgrading temporary bonding/debonding adhesive systems: Developing innovative solutions compatible with self-peeling, laser debonding, plasma cleaning, and microchannel-assisted unloading.
PSA for electronic films and flexible devices: Serving emerging applications such as foldable screens, wearable devices, and AIoT sensors, as well as personal care and medical devices.
Smart process integration: PSA integrated with big data automated production lines and industrial robots to achieve full-process monitoring, automatic bonding, and recycling.
Ultra-high cleanliness and ultra-low outgassing formulations: Addressing the extremely stringent cleanliness requirements of wafer-level packaging and aerospace components, as well as biological attack resistance for sensitive electronic and medical fields.
6. How to choose a silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive?
Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive is an important material for advanced processes such as semiconductor packaging, integrated circuit manufacturing, temporary chip transfer, and flexible electronics assembly. With its exceptional heat and cold resistance, insulation, purity, controllable adhesion/peel adhesion, and ease of automation, it adheres well to a wide array of substrates and provides a solid foundation for the modern microelectronics industry. As the global semiconductor industry enters a phase driven by both “domestic substitution” and “technological upgrading,” how can product competitiveness be enhanced?
XJY Silicone is one of China's leading manufacturers of silicone MQ resins and VMQ silicones, with over 30 years of R&D and manufacturing experience in the silicone industry, holding more than 15 related patents and technical support. Our silicone raw material products can meet the needs of the silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive field and provide diversified, customized solutions for qualified industrial users.




