Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives are suitable for many applications. However, we do not understand its bonding mechanism. In the bonding mechanism of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives, some literature says that the increase of the proportion of silicone can increase the peel adhesion of PSA glue. What is the reason? What does silicone adhesive rely on to bond the adherend?
The bonding mechanism of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives is as follows:
When the silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives are under appropriate and slow pressure, it produces a viscous flow similar to that of a liquid, so that the silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives are in close contact with the surface of the adherend and flow into the depressions on the surface of the adherend. Increase the effective contact area to produce a certain amount of adhesion. When the pasted pressure-sensitive adhesive product is peeled off by external force, the adhesives exhibit properties similar to elasticity and have a higher resistance to peel adhesion. The higher the peeling speed, the better the silicone adhesive product, the higher the adhesive strength. The wettability of the silicone PSAs on the surface of the adherend can make it and the surface of the adherend achieve the degree of molecular closeness, produce intermolecular force, and produce sufficient interfacial adhesion.
After finishing the bonding mechanism, let's take a look:
- How many kinds of silicone PSA does have?
- What is the preparation mechanism of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives?
- Why choose silicone PSAs?
- Application of silicone adhesives
How many kinds of SPSA do have?
Usually, there are three kinds of SPSA: high solid content SPSA, silicone PSA without aromatic solvent, solvent-free SPSA.
1. High solid content SPSA
Silicone PSAs are usually provided as solvent-based formulations because of its ease of handling during production.
Silicone PSA contains approximately 40~50 wt% of toluene or xylene. Lowering the organic solvent to silicone ratio in the formulation enables the reduction of organic solvent in exchange for a higher viscosity. This is because of the increasing MQ resin ratio in the formulation. Lowering the viscosity of the gum itself will help with lowering the viscosity of the overall mixture.
Peroxide cure type PSAs benefit from higher Mw gum for shear adhesion. Additionally, cross-linking is required for better performance. Increasing the amount of BPO could be a solution, but the maximum cross-linking density has a limiting threshold even if BPO is overused. Lower Mw gum helps decrease the viscosity of the formulation, but share adhesion is worsened.
In addition to cure-type PSAs, cross-linking density can be controlled by changing the number of vinyl groups in the gum. This results in the ability for addition cure type PSAs to have a high cross-linking density while achieving a low Mw gum with good shear adhesion.
2. Silicone PSA without aromatic solvent
Conventional silicone PSAs are made with aromatic solvents such as toluene and xylene because MQ resin is manufactured in these solvents. Toluene has acute toxicity as well as irritation to the mucous membranes when exposed to toluene. Xylene, like toluene, is toxic but is also carcinogenic with 2-ethylbenzene.
We tried to use isoparaffin, which is free of toluene and xylene, for the production of silicone PSA. Isoparaffin has the benefit of being non-irritative, as it is a compound found in cosmetic applications. It has the added benefit of having good performance for wetting the backing via lowering of the surface tension.
In peroxide cure type PSAs, polar solvents like methyl isobutyl ketone, ethyl acetate, or propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate should be used with isoparaffin because isoparaffin cannot dissolve BPO.
Addition cure type, Mw of gum can be decreased, so the viscosity of PSA can be lower. Conventional silicone PSA should be 40% content or lower for coating, however, PSA using lower Mw gum can be coated with 70% content.
Little solvent remains in PSA after cured, so toluene and xylene would stay little in cured PSA layer for conventional silicone PSA. In order to avoid the issue, we have to make MQ resin in organic solvent without toluene or xylene. It is possible to make MQ resin in isoparaffin technically.
3. Solvent-free SPSA
There is a market demand for reducing solvents found in cured layer of PSAs in applications like electrical insulation tapes, heat resistant tapes, masking tapes and carrier tapes for electrical devices when in use for closed working space like cleanrooms.
Removing all solvents from silicone PSA formulations lowers fluidity at RT. The 210,000 Mw gum measured has a lower than usual Mw gum that is for general PSAs.
As mentioned, PSA properties do not change with different Mws if cross-linking density is kept constant, however, using lower Mw base polymer that is functionalized with vinyl groups leads to a higher crosslinking density, which results in a PSA that is less soft and therefore has less adhesion.
Low adhesion silicone PSA can be obtained in solvent-free formulations by controlling the base polymer’s Mw and ratio of gum/MQ resin. PSA properties of low adhesion type and super low adhesion type are in Table 2.7. These types of PSAs can be coated without organic solvents. In addition, it is possible to coat a thicker layer and can form more than a 10 mm thickness of cured material. It can be applied as a gap filler between glass and flat panel displays.
Compared with conventional silicone PSA, these types of PSAs have lower viscosity. For tape applications, toluene-free primer for silicone PSA is also available.
What is the preparation mechanism of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives?
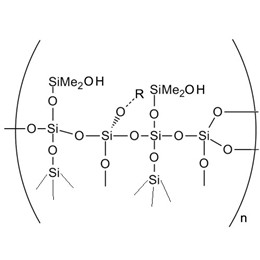
Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives are mainly made of a mixture of incompatible silicone rubbers, crosslinkers and other additives. Silicone rubber contains one or more polydiorganosiloxanes consisting essentially of hydroxyl or vinyl-terminated R1R2SiO bonds, usually containing Me2SiO units, PhMeSiO units and Ph2SiO units or two units.
The silicon-oxygen bond in the silicone rubber molecule is easy to rotate freely, and the molecular chain is easy to bend to form a helical structure, of which 6-8 silicon-oxygen bonds are repeating units [but the basic component of silicone adhesives is the continuous phase. Film formation can provide strength and provide necessary cohesion for silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives. Silicone is a dispersed phase used to improve the viscosity of adhesives, act as a tackifier and adjust the physical properties of pressure-sensitive adhesives.
As a matrix component of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives, silicone rubber is a linear polysiloxane in which silicon-oxygen atoms alternately form a main chain. Silicone rubber structure of pressure-sensitive adhesive. It is usually a colorless and transparent viscous liquid or semi-solid at room temperature, with an average molecular weight between 150,000 and 500,000, and a glass transition temperature Tg of about -120°C.
In the process of preparing silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive tape, the glue must be cross-linked with benzoyl peroxide. Vulcanization characteristics of benzoyl peroxide (BPO) vulcanized silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive: First, the vulcanization process is divided into two stages. In order to prevent the BPO from reacting with the diluent solvent, the solvent must be removed at low temperatures (80-100°C, then 150°C). Vulcanize for 5 minutes or vulcanize at 180°C for 3 minutes.
Secondly, the vulcanization temperature is relatively high, so the material of the silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive tape substrate is limited by heat resistance. By using 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl peroxide instead of BPO, the vulcanization temperature can be lowered. 140°C. Third, the standard amount of BPO is 2%-4%. Within this range, the adhesive amount of the silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive can be adjusted by the amount of BPO, and the adhesive force of the silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive can be reduced.
Why choose silicone PSAs?
Currently, environmentally friendly products consist of high solid content or non-aromatic solvent type. This lead to the goals of silicone PSA R&D which are to make “environmentally friendly” and “better performance” adhesives. Silicone PSAs can stick various surfaces making the area of applications wider if solvent-free type PSAs can be achieved from a technical standpoint.
We know that silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives generally refer to adhesives with silicone polymers as the main body, or acrylic and silicone-modified rubber-based pressure-sensitive adhesives modified by silicone polymers. Compared with traditional acrylic PSA (acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesive) and rubber-type adhesive, it has excellent chemical resistance, moisture resistance, oil resistance, high and low-temperature resistance, heat resistance degradation, and oxidation degradation resistance. Glue with a variety of difficult-to-stick materials such as non-surface-treated polyolefin (BOPP, PET, PE, etc.) fluoroplastics, polyimide, and polycarbonate.
Silicone adhesives made from PDMS will be improved adhesion to surfaces, show high heat resistance, good low-temperature resistance, tack, weatherproofing, shear strength, good electrical insulation and good chemical performance to many substrates. These PSAs are coated on various backings and made for PSA products like tape. It consists of high molecular weight (Mw) PDMS and MQ resin, which is provided solvent-based type using toluene or xylene.
Application of silicone adhesives:
- For high heat resistance applications: heat resistant tapes, masking tapes for electrical device/plasma/solder substrates
- For adhesion to the various surface: splicing tapes for silicone release liner, tapes for silicone rubber/fluoro resin/polyolefin substrates
- In electronics industry: binder for mica tapes, electrical insulation tapes
- Low reactivity to living organisms: skin contact application
- Removability and transparent: protective film for optical applications
|
Melamine tape |
PET film |
Medical application |
High temperatures green tape |
|
PTFE |
PI tape |
Fiberglass cloth tape |
Protective films-plastic films |
XJY Silicones
XJY Silicones is one of China's leading silicone manufacturers with more than 30 years of experience in the silicone industry.
We manufacture and customize different peel adhesion of silicone adhesives. Our XJY-301/302 series silicone SPAs technologies had obtained the ISO9001 certificate.
Confirm more about our product information? Contact us Now!