There are many wood coatings: oil-based finishes, solvent-based finishes and water-based wood coatings. And during the construction of the waterborne wood coatings market, It is generally recommended to apply "thin coating" multiple times This is because the drying speed of water-based coatings is slow, the hardness increases slowly, and it is difficult to achieve good construction results. However, in practical production and application, in order to improve the production efficiency, water-based wood coatings are required to be thick-coated at one time, especially in some areas where the requirements for board surface are not very high, such as the coating of window frames, frames and other wood surfaces. This application has been quite common.
This field is characterized by medium pressure mixed gas spraying, simple process and high production efficiency. The construction is characterized by high viscosity and one-time thick coating up to 250 μm. When using this process, one of the most difficult problems is defoaming.
During spraying, a large number of bubbles cannot be eliminated in the process of film drying, resulting in a large number of pinholes on the plate surface.
This has almost become an important resistance to the expansion of waterborne wood coatings to other professional fields such as furniture, especially varnish, of which 70% - 90% is resin, which makes defoaming much more difficult than solid paint (including titanium dioxide and other powders). In the coating of doors and windows, about 2 / 3 is matte varnish coating. Therefore, it is very necessary to study the defoaming performance of water-based matte varnish in medium pressure gas mixture spraying.
Factors affecting defoaming of Waterborne Wood Coatings industry
5. Matting powder and wetting and dispersing agent
6. Design and control of production process
XJY Silicones -- first choice silicone manufacturer for coating

The way foam producing
Foam during production
 | In the process of coating production, it is often necessary to disperse raw materials at a high speed so that the components are mixed evenly, so a large number of bubbles are generated. If these bubbles cannot be removed after being placed, it will inevitably affect the elimination of foam during construction. |
In the production process of water-based wood varnish with high resin content, it is difficult to eliminate foam when the viscosity is high, and in order to meet the needs of construction and storage, the viscosity must not be too low. If a medium-pressure air-mixed spray gun is used for construction, the construction viscosity is generally above 80KU. At a viscosity of 90KU (30°C), it is not difficult to simply solve the defoaming problem. However, in the actual production process, it is necessary to improve the thixotropy of the coating due to the problem of sagging the thick coating on the facade during construction. The increased thixotropy makes defoaming more difficult. Therefore, a balance between rheology and defoaming is required during the production of coatings.
On the other hand, formulating a suitable production process can also greatly reduce the bubbles generated during coating production. For example, in the production of matte varnish, the matte powder is first made into a slurry to avoid a large number of bubbles generated by high-speed dispersion when the matte powder is dispersed in the resin, add an appropriate amount of defoamer with good anti-foaming properties before starting the stirring, adjust the coating to the appropriate viscosity before high-speed dispersion, to avoid bringing a lot of air into the coating when the dispersion liquid level oscillates, etc. All of these can reduce the generation of air bubbles in paint production.
Foam during construction
1. Substrate
When painting wood coating, since the wood surface itself has many capillaries, the substrate is often sealed first. If the substrate is not well sealed, the air in the capillary of the wood grain substrate will escape during the coating construction and enter the wet film of the coating to form bubbles. If the bubbles cannot be broken, pinholes or craters will be formed. In the construction process of water-based coatings, especially in the fully enclosed coating, due to its high construction viscosity, one-time spraying is thick, which makes it more difficult to defoam the wet film of the coating during construction. Therefore, in the fully closed coating of water-based coatings, generally, 1 to 2 closed primers are required to drive out the air in the capillary of the substrate as much as possible. Otherwise, once the air enters the thick coating of the subsequent process, the bubbles formed will be difficult to eliminate.
2. Airbrush
Construction tools are also a factor in the formation of bubbles in the paint. In the construction of water-based furniture coatings, the primer and top coat of the middle coat are all applied by spraying. Generally speaking, the better the atomization, the less likely to generate air bubbles during construction. Therefore, the effect of spraying with an air cup gun is better than that of medium-pressure mixed air spraying. There are two main reasons: First, the atomizing air pressure is relatively large when spraying with an air cup gun, generally 0.6-0.8MPa, and the paint is fogged. After spraying, it reaches the surface of the construction object at a high speed, so that even a small amount of air bubbles can be broken when the paint liquid particles "hit" the surface of the object, while the atomizing air of the medium-pressure mixed air spray gun is only 0.1 ~ 0.2MPa, its The atomization effect is worse than that of the air gun, and the speed of the paint liquid particles reaching the surface of the object is also lower than that of the air gun, so the foam breaking during the construction process is poor. Second, the viscosity of air gun spraying is lower than that of the medium-pressure air-mixing spray gun, which also makes the atomization and foam breaking off the paint liquid during the construction of the air cup gun easier and the defoaming in the later surface drying process.

On the other hand, the adjustment of the oil and air volume of the spray gun during construction is also an important factor affecting the generation of air bubbles. Whether it is an air spray gun or a medium-pressure air-mixing spray gun, the oil volume and air volume can be flexibly adjusted, and the proportion of its deployment depends on the viscosity of the paint or the construction effect to be achieved by the object to be coated. For example, in the construction of semi-open coating, it is sometimes required to spray "dry" (small oil volume and large air volume), while in the fully closed coating, it is generally necessary to spray "wet" (a slightly larger oil volume and a large air volume). slightly smaller). Generally, I should be applied before construction by adjusting the amount of oil and gas to make the paint atomization reach the best state, so as to achieve the best construction effect.
Factors affecting defoaming of Waterborne Wood Coatings industry
1. Resin
In the defoaming experiment of water-based high-viscosity matte varnish, the resin is the most critical factor affecting the difficulty of defoaming. At present, there are three main types of waterborne wood coatings, waterborne polyurethane (PU), waterborne acrylic (AC), waterborne polyurethane and waterborne acrylic composite (PUA). Due to the different synthesis mechanisms, the defoaming difficulty of the three types of resins is also quite different.
The defoaming of water-based PU and PUA is relatively easy, and the water-based AC is relatively difficult. This is because the former does not use or rarely uses an emulsifier in the synthesis process because the emulsifier itself is a kind of surfactant, which is easy to form when agitated. Bubble. However, in the domestic water-based furniture coating market, water-based AC products have been widely used due to their great advantages in price, drying speed, and water resistance. In particular, the core-shell polymer emulsion has a lower film-forming temperature, which greatly reduces carbon footprint and has a low VOC content, and has good hardness, elasticity and anti-blocking properties after film formation. It has been widely used in outdoor wood products surface coating. Pack.
In AC type emulsions, the types and synthesis methods of emulsifiers during emulsion synthesis are different, and the difficulty of defoaming is also different. Such as anionic emulsion system, the particle size is small, and it is easy to foam. The water-based AC emulsion using soap-free polymerization and core-shell polymerization is better than the traditional water-based AC emulsion in defoaming. Experiments show that the use of core-shell polymerized emulsions can greatly reduce the difficulty of defoaming in the production process when formulating high-viscosity matte varnishes.
2. Viscosity
The higher the viscosity of the coating, the more difficult it will be to defoam, whether it is being stored in the paints can or during the surface drying process after application. In actual production, in order to prevent sinking and sagging, etc., the coating should always be controlled within a certain viscosity range. In the medium-pressure air-mixing spraying of water-based wood coatings, it is necessary to ensure that the construction viscosity of the coating is 80KU or above, and the ex-factory viscosity of the finished product is often above 90KU to meet the viscosity changes caused by temperature rise and adding water during construction. Need to adjust viscosity. According to the different rheology of the coating, the viscosity of the coating should generally be controlled at 90 ~ 120KU (25 ℃)
3. Defoaming
In waterborne matte varnishes with high viscosity, defoaming is difficult because of its high resin content and high viscosity. In production, the dosage and types of defoamers are relatively large, generally, there are 2 to 3 defoamers to be used together, which play the role of anti-foaming, defoaming, and defoaming before, during, and after high-speed dispersion respectively. In order for defoamers and other auxiliaries to mix well with the resin, it must be dispersed at a high speed, which will produce a large number of bubbles. Therefore, it is very necessary to add a certain amount of defoamer with a good antifoaming property before high-speed dispersion.
There are two kinds of defoamers commonly used in waterborne wood coatings: mineral oil and silicone. The former has low cost and weak defoaming ability, which is mainly composed of 85% carrier oil and 15% hydrophobic particles. Hydrophobic particles are generally composed of fumed silica, stearic acid metal salts, and so on. This kind of defoamer is easy to blacken the film and can be used for low gloss putty and primer. The latter is mainly composed of strong hydrophobic silicone emulsion and polyether-modified polydimethylsiloxane, which has no effect on gloss and transparency and is the main defoamer for waterborne wood coatings. However, it is also pointed out that some mineral oil-modified defoamers are more effective than silicone defoamers. Therefore, the selection of defoamer should be based on different resins and experimental results.
4. Thickening agent
In the production of waterborne high viscosity matte varnish, the selection of thickener is very important, which is the key to the defoam ability of the product during storage or construction. At present, there are two kinds of thickeners commonly used: Association type and alkali swelling type. The former can provide better leveling and shear viscosity, while the latter can improve the storage stability and anti-hanging property. In production, the former is beneficial to defoaming and defoaming, while the latter is easier to stabilize bubbles.

However, because the former has good fluidity, its anti-pollution ability during construction is greatly reduced, therefore, in order to maintain the storage stability of the coating, it has better anti-flow hanging and anti-pollution ability during construction. waterborne matte varnishes are sometimes matched with certain alkali swelling thickeners even at high viscosity. There are many kinds of these two kinds of thickeners, and how to match them depends on the experimental results after the resin is selected.
5. Matting powder and wetting and dispersing agent
In the water-based matte varnish sprayed by medium pressure air mixing, the matte powder is generally selected as a matting agent, rather than matting wax slurry. Because the medium-pressure air-mixing spraying does not have high requirements on the feel of the board surface, and at the same time, it should also consider defoaming, price, and system thickening reasons. The cost for using matting wax slurry (powder) is high, and it is easy to produce foam during dispersion, and it is difficult to eliminate.
In high-viscosity varnishes, the anti-settling of the matting powder should be ignored, but it’s important for the defoaming property. Generally, the hydrated surface is easier to defoam compared with the untreated surface, and less oil absorption is easier to deform than the larger oil absorption. Experiments show that the selection of different wetting and dispersing agents has a great influence on the defoam system. The better the dispersing agent wets the surface of the matting powder, the more conducive to the defoaming of the system.
6. Design and control of production process
In coating production, the design and control of the process are also very important. In the production of water-based coatings, in order to mix the resin and other components uniformly and generate fewer air bubbles, it is necessary to formulate a suitable production process and strictly control it.
For example: in the production of matte varnish, additives and matting powder are generally added to the resin and then dispersed with high speed. During the process, a large number of air bubbles will be generated. When the viscosity is low, bubbles will be eliminated after lasting for 24 hours, but when the viscosity is high and the system with strong changeable ability, it is difficult to eliminate these bubbles for a long time. At this time, the matting powder is made into a slurry and added, which can effectively reduce the generation of foam. On the other hand, when adding defoamer or other additives that are not easy to disperse, it is best to dilute them and add them slowly in a dispersed state to minimize the speed required for dispersion and reduce the time for uniform dispersion; some are easy to foam additives such as some wax slurry, etc., should be added in later low-speed dispersion process as much as possible.
Conclusion
 | The high viscosity construction of waterborne wood coatings can improve the one-time construction thickness, improve the production efficiency, and reduce the possibility of sagging and bubbles during construction, but it increases the difficulty of defoaming during construction, greatly affects the board surface effect after construction, and becomes the main resistance to the expansion of waterborne wood coatings to other application fields. |
In the study of defoaming of waterborne high viscosity varnish, the selection of resin and thickener is the most important, followed by the selection of defoamer, matting powder and other additives, and finally the optimization of the production process and the adjustment of viscosity. A good product should not only have good physical and chemical resistance properties but also have good construction performance. Only when the two are well combined, can it show excellent coating effect and meet consumption requirements, and the development of waterborne wood coatings will be more rapid.
XJY--First choice silicone supplier for coatings
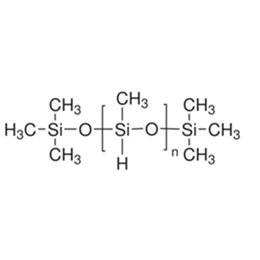
XJY-701 Polymethylhydrosiloxane: coating leveling agent
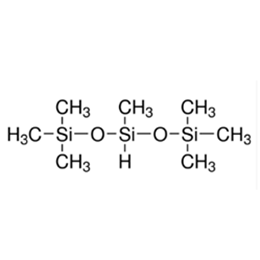
XJY-703 Heptamethyltrisiloxane: coating additives
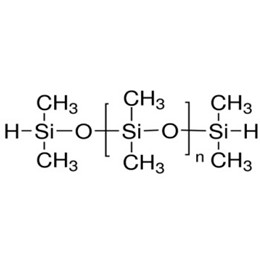
XJY-707 Hydride Terminated Polydimethylsiloxane: coating additives
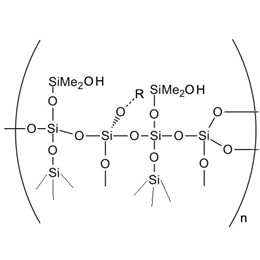
XJY-8205 Silicone MQ Resin: industrial tackifying, waterproof
XJY-8205M Silicone MQ solution
XJY-801 Polymethylsilsesquioxane: improve lubricity, scratch resistance, dispersibility and hydrophobic