Construction sealant is a kind of paste of basic adhesive, filler, curing agent, and other additives to form an elastomeric sealants material in the construction industry, after playing the use will be cured into an elastic rubber material, bonded to the building substrate, play sealing properties, waterproof and leak-proof role, mainly used in the building mechanical joints caulking seal. As a kind of construction adhesive, it is significantly different from other construction adhesives such as glue in form and application, other construction adhesives are generally fluid, mainly used to bond, and paste the building decoration materials, is no sealing properties.
Next, we are going to talk more information about it
- How are construction sealants classified
- Silicone construction sealants
- Silicone construction sealants
- The main performance of the sealant
- Methods of evaluating performance properties of sealants
1. How are construction sealants classified
1.1 According to the role played by different:
One is the construction of structural sealants, and the other is non-structural sealants. Structural sealant is also referred to as structural adhesive, which is used in the production of curtain wall units for structural bonding and sealing of glass, window and door perimeters, and other building panels in construction industry, which are completely bonded to the frame by structural adhesive, with no other fixed connections. Therefore, structural adhesives have strict requirements for strength and adhesion.
Non-structural sealant is other than structural adhesive construction sealant, the role of this type of adhesive is to seal the joints (expansion joints, vertical joints, horizontal joints), not structural bonding, so there are no very strict requirements for strength, as long as it can be better adhesion in the various substrates to have sealing properties to prevent fluid. As to take into account the impact of thermal expansion and contraction of the substrate on the expansion and contraction of the joint width, the sealant must have good elasticity and displacement capacity.


1.2 Chemical Composition
A more common classification method is by chemical composition. According to the chemical composition of the base rubber for sealants, sealants can be divided into polysulfide sealants, polyurethane sealants, silicone sealants, neoprene sealants, butyl rubber sealants, acrylic sealants, and other sealants. The current market is a large amount of silicone, polyurethane, and polysulfide three categories. Environment requirements for three types of sealants on the content of volatile organic compounds have clear requirements, China's provision of silicone sealants needs to meet the volatile organic compounds content of less than 100g/kg of environmental indicators. (Among them, the silicone sealant is stable, with superb UV resistance, ozone resistance, weather aging resistance, temperature resistance, and one-component, two-component multiple forms of application, at the same time can be manufactured according to the needs of the building of the different performance requirements of the product, the application of silicone sealants more in China. And XJY-8206 Methyl VMQ Silicone Resinis widely used in the construction industry because of its good reinforcing performance and hardening effect.)
1.3 Component Packaging
Construction sealant is divided into single-component and two-component packaging according to the classification of packaging.
Single-component packaging is the composition of all the raw materials of sealant mixed, sealed packaging in a plastic bottle or flexible packaging aluminum film, when using the product from the packaging with a glue gun to play out can be.
Two-component packaging is composed of two components, A and B. Generally, component A is the base adhesive material, and component B is the curing agent. Fillers and other additives are added in components A and B as needed. When using, special mechanical equipment (two-component beater) is used to mix the A and B components in the prescribed ratio, and the A and B components are cured by chemical reaction, neither the A component alone nor the B component alone can be used.


1.4 Curing Characteristics
Sealants can be divided into different classifications such as chemically reactive, solvent-volatile, and hot-capable cold-setting according to curing characteristics. Silicone sealants belong to the chemical reaction type.
2. Silicone construction sealants
2.1 How are silicone construction sealants classified?
Silicone construction elastomeric joint sealants are cured by chemical reactions to condense and release volatile small molecules, according to the different chemical reactions that are different to release small molecules can be classified again for these products. There are two types of products in circulation in the market: one is acid glue, which is acidic, and the small molecule released during curing is acetic acid, which has an acid smell and is corrosive to some metal materials, and is also irritating and corrosive to the human body. Another type of silicone sealant is neutral glue, which is neutral and divided into alcohol glue and ketoxime glue according to the small molecules released during the curing process. The alcohol-type glue and the small molecule released during curing is methanol, which has no corrosive and irritating odor. The ketoxime adhesive emits ketoxime during curing, which is more odorous than the alcohol-based adhesive. These two types of silicone sealants are different in odor and nature.
2.2 How to produce silicone construction sealants?
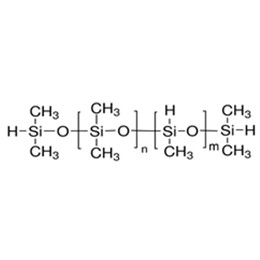
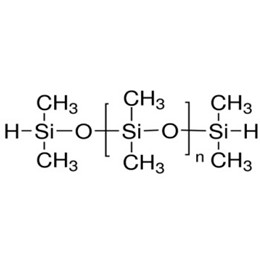
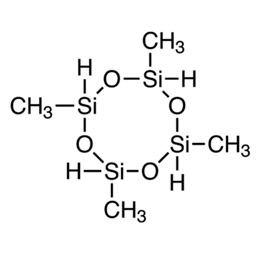
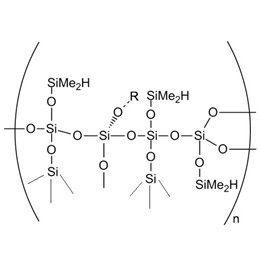
Silicone elastomeric sealants mainly has base adhesive, filler, and cross-linking agent(just as XJY-705 1,3,5,7-Tetramethylcyclotetrasiloxane/XJY-707 Hydride Terminated Poly Dimethylsiloxanes, both can be used as special crosslinking agents), catalyst and other components providing a protective impermeable barrier. The base adhesive is the basic material of the sealant, which determines the performance of the sealant. Base rubber is 107 room temperature vulcanized silicone rubber, the chemical structure is end-hydroxy polydimethylsiloxane, and the filler is some inorganic powder, such as silica, calcium carbonate, heavy calcium, etc. (XIY-8207 S/M Hydrogen MQ Resin can be used as a reinforcing filler for RTV adhesive to be added into construction sealant.) The role of filler is to provide strength, hardness, rheological properties, etc. Cross-linking agents and catalysts are the curing system of sealant. The sealants are changed from the liquid state to elastomeric joint sealants by the reaction of base rubber with the cross-linking agent and catalyst and water in the air. It can also be made into low modulus sealants according to the recipe.
The production process of sealant is the process of mixing two or more components of the sealant. The usual method of production is to mix the base material and filler with a kneader and, if necessary, with a grinder, and then to mix the cross-linker, catalyst, and other additives under vacuum with a planetary machine.
2.3 What are the properties of silicone construction sealants?
Compared with other sealants type(such as polyurethane sealants, acrylic sealants, and other sealants ), as elastomeric sealants, silicone construction sealant elasticity, high-temperature resistance, sealing properties, and low-temperature flexibility are better, weather resistance, ozone resistance, and UV resistance are better, and long service life, is more suitable for the construction industry, but the relatively high cost of silicone, is usually a little more expensive than other varieties of sealants, strength, especially the strength of tear resistance is poor, there is information about water resistance than polyurethane sealants is worse than some, oil resistance is not as good as Polysulfide sealant, acrylic sealants have better viscosity. And the exact choice depends on main application of the sealants in the construction industry.
2.4 How does silicone construction sealant cure?
Single-component sealant sealed package in the container is stable, from the container out of the exposure to the air will cure. This is a chemical reaction process, the sealant is originally a paste, and after contact with air, the sealant base glue, cross-linking agent ( XJY-711 Hydride terminated methyhydrosiloxane dimethylsiloxane copolymer can also be used as a crosslinker for silicone rubber applications, is one of the main raw materials for elastomeric joint sealants), catalyst and the water in the air chemical reaction, the result of this chemical reaction is to make this paste gradually into an elastic solid, which is the sealant curing. After the sealant is beaten out, the surface of the sealant is the first to be exposed to water, so the first to be cured is also the surface. After the surface is cured, the water will seep in from the cured surface, the inside layer will be cured again, and the sealant will be cured gradually from the surface to the inside. The thicker the sealant, the longer it takes to fully cure, for example, 10mm thick adhesive, usually takes more than a week to fully cure.
Two-component sealant is carried out by chemical a reaction between components A and B. Components A and B are stored separately for sealing and are stable, once components A and B are mixed, they start to react, so components A and B should be used immediately after mixing. The curing reaction of two-component does not require the participation of water in the air, so it is cured by both internal and surface at the same time. The complete curing time is not related to the thickness of the adhesive, so the reaction is also not related to whether it is in contact with air or not, as long as the A and B components are mixed, they will be cured even in an airtight state.


2.4.1 Performances of sealant curing performance
Surface drying: The sealant is paste-like when it is beaten out, and the adhesive will adhere to the fingers or other materials when they touch its surface. After the sealant is beaten out, the surface contact with water starts to cure and crust, when the skin is formed, then when the finger or material touches the surface, there will be no more adhesive adhering to the finger or material. This is called surface drying.
Surface drying time: The time it takes for the sealant to dry is the surface drying time from the time the sealant is punched out of the container.
After the sealant is dried, the surface is touched by the finger, although there is no adhesive material adhering to the finger, but still can feel the adhesion between the adhesive surface and the finger, this phenomenon we call not yet eliminated sticky. This is the performance that the curing reaction of the adhesive surface has not been carried out completely. With the extension of time, it will be further cured until the surface forms a layer of elasticity and strength of the skin, and the finger contact feels dry, with no feeling of adhesion, we call it the elimination of sticky.
The elimination of sticky time: sealant from the container out of the beginning of the time, to its surface of the time required to eliminate sticky, is the elimination of sticky time.
3. What factors will affect the curing performance of sealants
Environmental factors have a very obvious effect on the curing performance of sealants. First is the impact of temperature, the higher the temperature, the faster the curing reaction rate, the phenomenon is the surface dries, elimination of sticky id faster, if the temperature is very low, such as 5 ℃ below, the sealant curing will be very slow. And if the temperature is too high, such as 40 ℃ or more, the sealant will be too fast because the surface is dry and inconvenient to use.
Humidity also has a significant effect on the curing performance of sealants, because the sealant curing reaction requires water in the air, so too dry weather, such as relative humidity below 40 ℃ on the sealant curing is not good. But not the higher the humidity is better, because the sealant curing releases volatile small molecules, if the air humidity is too large, small molecules will not be easy to volatilize, which is also not conducive to sealant curing. Experiments have proved that when the relative humidity is higher than 80 ℃, sealant elimination of sticky and deep curing will be affected, sometimes after 2-3 days, the surface of the sealant and sticky.
The standard conditions for the performance of sealant as stipulated in the national standards are temperature (23±2)℃ and relative humidity (50±5)℃.


4. The main performance of the sealant
In addition to the curing performance mentioned above, the following performance items are also important:
(1) Appearance:
The appearance of the sealant mainly depends on the dispersion of the filler in the base adhesive. The filler is a solid powder, after the kneader, grinder, and planetary machine dispersion, it can be uniformly dispersed in the base rubber to form a fine paste, sometimes according to the nature of the filler itself, does not exclude the existence of a very small amount of fine particles or fine sand, which is an acceptable normal phenomenon. If the filler is not well dispersed, there will be a lot of very coarse particles. In addition to the dispersion of filler, some other factors will also affect the appearance of the product, such as mixing with granular impurities, crusting, etc. All these conditions will be considered as coarse appearance. The appearance of observation method is the product from the packaging out of direct observation, or the product will play 1-2g in the white paper, fold the white paper flat and then open the observation, the term called "butterfly observation". When coarse grains are found, the coarse grains should be judged.
(2) Hardness:
Hardness refers to the hardness of the sealant after it has completely cured into a rubber body, which is one of the physical and mechanical properties of the product. Hardness refers to the ability of the material to resist attempts to scratch or press into its surface. According to the different methods of measuring hardness, the hardness is expressed in a variety of methods such as Brinell hardness, Rockwell hardness, and Shore hardness. The national regulations use Shore A hardness. The standard hardness value is detected by making specimens with hardness tester according to the national standard method. Sealant hardness is high, but the surface sealant rigidity, elasticity, and flexibility are not enough; hardness is small on the contrary, elasticity and flexibility are good, but rigidity is not enough. Therefore, the sealant is not the harder the better, nor the softer the better, but according to the actual needs of a certain range of requirements.
(3) Tensile strength:
tensile strength is also one of the mechanical properties of the sealant after complete curing. Tensile strength is also known as tensile strength, and tear strength, is commonly known as tensile strength. The material can resist damage when under tension. The tensile strength value is also detected according to the method specified in the national standard. Sealant according to the needs of its use is to have a certain strength requirement, especially the structural adhesive, but also in the national standards specify the minimum value of strength, strength is too poor sealant can not meet the needs of use. However, the excessive emphasis on the strength of the sealant and ignoring the elasticity is not aggressive.
(4) Elongation:
elongation is the sealant that is fully cured after the elastic performance, also belongs to one of the mechanical properties, which refers to the total elongation of the material in tension and the percentage of the ratio between the original length. A good elastic sealant will have a large elongation. As the minimum requirement of elongation, the sealant must meet the requirements of the national standard for fixed elongation performance.
(5) Tensile modulus and displacement capacity:
tensile modulus and displacement capacity is a comprehensive performance of the above mechanical properties. Tensile modulus is characterized by the strength of the sealant when stretched to a certain elongation. Therefore, the touch is expressed together with the elongation, such as elongation of 25% when the tensile touch is 0.46 Mpa. displacement capacity indicates the sealant's capacity to withstand displacement due to thermal expansion and contraction of the base material resulting in seam dislocation. For example, we say that the sealant has ± 25% displacement capacity, shows that the use of the product can withstand 25% of the original width of the seam stretching and compression, such as the original width of the seam is 12mm, it can be compressed to a maximum of 9mm, stretching to 15mm. displacement capacity can be detected by the stretching and compression cycle or cold pulling and hot pressing cycle method.
(6) Adhesion to the substrate:
This is a very important performance in the actual use of sealant, sealant must have good adhesion to the actual use of the substrate to use. The easy way to test the adhesion is to clean and dry the substrate with appropriate solvents or detergents, and the sealant will be placed on it, after the sealant curing (about 3-5 days), peel the sealant by hand to observe the bonding situation.
(7)Extrusion:
This is a project of sealant construction performance, used to indicate the ease of sealant use when playing the degree of difficulty, too thick rubber extrusion is poor, and the use of the glue is very laborious. But if you simply consider the extrudability and the rubber is too thin, it will affect the thixotropy of the sealant.
(8) Thixotropy:
This is another item of sealant construction performance, thixotropy is the antonym of fluidity, which means that the sealant will change its shape only under certain pressure, no external force can maintain its shape, and will not flow. The national standard for the determination of the sagging degree is the judgment of the thixotropy of the sealant.


5. Methods of evaluating performance properties of sealants
How can we choose the most suitable sealant? Sealant from the bottle into a strip, in the process of glue and the observation of the strip can be tested or simple judgment of the following properties.
(1) Extrudability: The extrudability of the glue can be felt initially by the difficulty of the glue.
(2) Curing performance: After the glue strip is beaten, the surface drying time, the elimination of sticky time, and the complete curing time can be measured to determine whether the curing performance is normal.
(3) Thixotropy: After the adhesive strip is beaten, the surface sealant is qualified for thixotropy if it is placed horizontally without deformation, and if it has the phenomenon of flowing and deformation, it shows that the thixotropy is not good.
(4) Hardness: After the adhesive strip is completely cured (generally about 1-2 days), you can feel the hardness of the adhesive strip by pressing it with your finger, and the method can be relatively compared to the hardness.
(5)Strength, elasticity, and elongation: pulling the fully cured tape can make a relative judgment on the strength, elasticity, and elongation. This experiment must be noted: we usually play the tape on the paper, from the paper after tearing off the tape, often in the tape on the sticky layer of paper, if this pulling tape, because the paper is not elastic, a pull will tear, while the sticky tape on the paper will also tear open a mouth, due to the silicone sealant tear strength is generally low, the stress generated by stretching will be concentrated in the tear, it is easy to From here to pull off the tape, affecting the observation and judgment. The correct practice is to beat the adhesive strip on the plastic film and pull the adhesive strip to judge the performance after it is completely cured.
XJY Silicones - the preferred raw material supplier of silicone construction sealants
XJY Silicones, one of China's leading Silicone MQ resin and VMQ silicone manufacturers, has 30+ years of R&D and manufacturing experience and 15+ related patents in the silicone industry, also can customize the cost-effective raw material products for construction sealants according to your molding process and specification requirements.