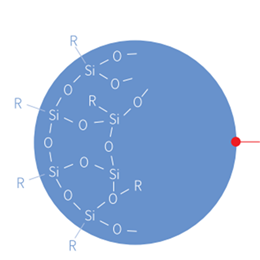
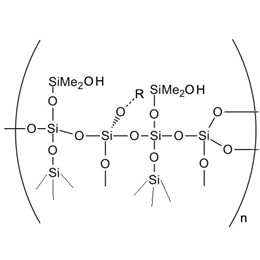
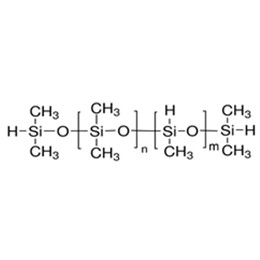
Compared with traditional coatings, UV coating refers to the coating cured by ultraviolet light. UV curable coatings can be applied to ink printed materials and exposed to ultraviolet radiation. UV coating offers solid content that can be as high as 100%, so it does not emit volatile organic compounds and does not pollute the environment. High solid content can also be used in a very thick layer. But how to select coating resin effectively in the UV coating formulation, is a question.
Characteristics of the gloss UV-coated curing reaction
Brief introduction of resins commonly used in UV coatings by function
4. Aqueous coating UV oligomer
5. Application of non-crosslinking class resins in the UV coating process
2. Toughness (hardness and wear resistance)
XJY Silicones - First choice raw material supplier of silicone coating application
Characteristics of the gloss UV-coated curing reaction
UV ultraviolet coating curing is a polyaddition reaction between unsaturated molecules. According to the initiation mechanism of the initiator, there are free radical polymerization and cationic polymerization. But the common polymerization we study is free radical polymerization (this lecture is based on free radical polymerization). The last C-C cross-linked structure is a rigid cross-link.
Polymerization mechanism
Radical polymerization has a rapid reaction; large shrinkage; a small change in polymerization degree; the large influence of polymerization inhibition (0.01-0.1% polymerization inhibitor prevents the reaction).
--The most unfavorable thing for coatings is shrinkage. According to foreign studies by W.J.Bailey, etc., it is found that the non-polymerization time of double bonds is 11%.
Brief introduction of resins commonly used in UV coatings by function
Hard resin - high Tg
Soft resin—low Tg
Polar resins
| Oligomers containing reactive hydrogen or easily forming hydrogen bonds, changing polarity or surface tension
|  |
Aqueous coating UV oligomer
| Emulsion type, water dispersion type, water-soluble type
|  |
Non-crosslinking class resins in the UV coating process application
Filling role, improve cross-link density, increase adhesion, change flexibility, enhance wettability, and other auxiliary roles
- Long oil alkyd resins.
- Thermoplastic acrylate resins.
- Aldehydes and ketones resins.
- Petroleum resins, etc.
Selection of primer resin
- Adhesion requirements
This is the generality of the primer resin, relatively speaking at present it is difficult to adhere to the main are.
A. glass ------ choose methacrylate oligomers and non-film forming resins and some special polar resin - thiol siloxane system with (but water resistance is a barrier to the current formulation);
B. metal, divided into metal types, for the adhesion of metal in the coating industry is basically applied to destroy the cross-linking method, the international common is phosphate treatment. UV is currently the most common is phosphate ester combined with some pure propylene methods.
C. plastic class (including plasticized paper and other types of paint finishing), which is currently a relatively large class of the particularly complex class, mainly because of the complex structure of plastic, crystalline form, surface tension varies, relatively difficult BMC, PET, PP, etc. There is no unified formula that can be eaten, generally speaking with soft PUA, and pure C and some non-film-forming resin and polar resin have some effect, but we should pay attention to chemical resistance, and water resistance to paying strict attention to the relevant resin with.
D. oil-containing wood: at present, mainly some hard sandalwoods such as clone wood, rosewood, greenshank mulberry, big hippopotamus wood, and other wood oil adhesion is relatively difficult, to seal the oil on the market is still very few pure UV good case, you can first use PU seal and then do UV adhesion primer. Mainly with some polar resin or monomer and filler resin can do a good job of adhesion.
- Wettability
The wetting of pigments and fillers and the wetting of substrates are two different functions because the surface tension of the substrate cannot be guaranteed to be exactly the same as that of the pigments and fillers.
A. The wetting of pigments and fillers can ensure the storage stability of the coating and the transparency of the compatibility of the paint film. For example, some PUA, PEA, and epoxidized soybean oil acrylate have this effect;
B. For the wetting of substrates such as amino resin and PEA, the effect is better.
- Flexibility
It is related to standability and interlayer adhesion.
Standard EA and some PEA and some monomers are generally selected to coordinate the flexibility of the treatment, thereby adjusting the sanding and interlayer adhesion.
At present, there are also hardened primers that emphasize hardness in the market - pay attention to the curing of the hard resin and the coating amount made by UV coating machine, otherwise, it will easily lead to the bursting of the paint film;
The market also requires so-called elastic primers - more flexible resins, preferably polyester PUAs, polyethers have poor toughness and insufficient mechanical modulus.
Choice of topcoat resin
Fullness and leveling
To meet this requirement, it is necessary to choose a resin with good compatibility and a monomer combination, improve the wetting and leveling with the primer, and appropriately increase the degree of cross-linking, and choose a resin with a higher refractive index.
Generally, high functional group PUA, amino resin and standard EA are used as the main resin.
Toughness (hardness and wear resistance)
There are many inevitable correlations between the two paint film properties, but they are not necessarily exactly the same, and they are treated differently.
Hardness: In addition to traditional wood lacquer coating with a thick paint film of 80-120Unm and some thick spraying, a large part of the hardness, in this case, comes from the paint film itself, and there is also a part of the false hardness that needs to be paid attention to, such as substrates, Primer coating, surface feel, etc., rolling surface and thin spraying are a typical example. In addition to the above-mentioned high-functional resin, some silicone resin or silicone additives can be used to improve.
Wear resistance: PUA will be better, mainly hydrogen bonds, which can provide some toughness to increase wear resistance. However, the wear resistance of the thin coating cannot be solved by resin.
Interlayer adhesion
Solve the wetting and leveling and resin polarity matching, Zengjian adhesion can be solved, and some methacrylate resins can be selected in special cases.
Chemical resistance
EA and PUA (polyester) have good chemical resistance, while PE and polyether are worse.
Yellowing resistance
It is generally believed that aliphatic PUA, pure polyether acrylate, pure propylene, and amino all have good yellowing resistance. The first type is everyone's favorite, but the yellowing resistance is not the best. The latter two types are rarely used because of the lack of items, but the amino with the best comprehensive properties of yellowing resistance.
Matte
At present, some resins with slightly smaller molecular weights or huge ones are effective, and other polyurethanes are also very effective (there is currently a bifunctional polyurethane with a good hardness on the market that is competitive).
XJY Silicones - First choice raw material supplier of silicone coating application
XJY Silicones, one of China's leading Silicone MQ resin and VMQ thermally conductive silicones manufacturers, has 30+ years of R&D and manufacturing experience and 15+ related patents and technical assistance in the silicone industry, also can customize the cost-effective silicone products according to your coating options.
![]()