Medical devices are instruments, equipment, apparatus, materials, and other related supplies used to diagnose, treat, alleviate, and monitor diseases. As technology continues to advance, more and more materials are being used in medical device manufacturing, and silicone is one of the most widely used materials.
Since 1960, due to the excellent properties of silicone rubber, especially excellent biocompatibility, and biological inertness, it has been increasingly used in the field of medical devices. What are the applications of medical silicone?
In the existing medical applications, short-term contact medical devices include human catheters, infusion tubes, laryngeal tubes, silicone binders, lubricants, etc.; long-term implantable medical products including artificial breasts, artificial joints, facial implants, and so on. The silicone gel in prosthetic applications to viscous local and transdermal wound care applications plays an important role; LED sensors and other electronic devices with multiple components such as encapsulation are also common applications of silicone.
Here's some information about it:
- What are the advantages of silicone?
- How to use silicone materials in the medical field?
- How to apply silicone in medical devices?
- How to make your medical silicone performance better?
1. What are the advantages of silicone?
Silicone is a widely used material in medical devices. Its excellent properties and multiple applications, ranging from breast augmentation materials to cardiac stents, bring better results and higher safety to the medical community.
![]()
(1) High-temperature resistance
Silicone materials are thermally stable and can withstand high temperatures. Thus it can be used in medical devices in high-temperature environments.
(2) High stability
Silicone materials have good physical properties
, can withstand chemical corrosion, are not easily dissolved or decomposed, and can be used in a variety of environments, but also have the stability of not being easy to deform. It can be made into a variety of devices through controlled processing.
(3) Biocompatibility
Silicone materials are biocompatible with the human body, will not cause allergic reactions or other adverse reactions, and are very suitable in medical devices. Silicone materials have good compatibility with cells and will not affect the form and function of cells, suitable for medical devices in the body.
(4) Moldability
Silicone materials have excellent moldability, can be made into a variety of shapes and sizes in the molding process, can be made into a variety of shapes and sizes, and are suitable for the production of different medical devices.
(5) Long service life
Silicone materials have a long service life and can be used for a long period of time, and they are not easily damaged, so they can maintain the function of the instruments.
![]()
2. How to use silicone materials in the medical field?
Depending on the composition, uncured silicone systems can have different properties and categories. From liquids and greases to clay-like rubbers, the wide range of material compositions makes medical-grade silicone a viable option for countless applications. Gels and elastomers are the most common types of silicones used in healthcare.
2.1 Silicone oils
Linear Polysiloxanes are fluid liquids within a certain range of molecular weights, and their viscosity increases with the molecular weight of the Polysiloxane, while the site-blocking or polarization effects of the functional groups on the side groups also have a significant impact, causing the viscosity of silicone oils to increase. Silicone oil used directly in industry does not contain reactive groups, and the side groups are mostly methyl, phenyl, amino, fluoropropyl, etc. It is mostly used as a lubricant and antifoam agent and is widely used in various fields.
XJY-706 Tetramethyldisiloxane is a colorless transparent liquid, non-toxic, and insoluble in water. It is soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum hydrocarbons, and other organic solvents, insoluble in water, due to the molecular structure containing active hydrogen atoms, and can be synthesized through the silicon-hydrogen addition reaction of the copolymer polymer, from which they can be made into a series of activated silicone oil, the product as a silicone hydrogen capping agent, reducing agent, is mainly used in the production of pharmaceutical and chemical industry.

2.2 Silicone gel
Linear polysiloxane side groups contain reactive groups, in the catalyst and under certain conditions, can be reacted with the crosslinking agent, crosslinked to form a soft and transparent silicone gel. The reactive groups on linear polysiloxanes include Si-OH, Si-O-Me, Si-O-Et, Si-Vi, etc. The cross-linking agents are silanes or siloxanes containing two or more functional groups, and the catalysts are Sn, Pt, amine, and so on.
Silicone gels are made from a two-part system of reactive silicone polymers and reactive silicone cross-linkers that produce little elastomeric strength. When cured, these low-viscosity materials have a soft, compliant feel, combined with the low modulus of silicone, allowing them to mimic human tissue. They range from very soft prosthetic applications to very tacky topical and transdermal wound care applications. The encapsulation of electronics such as LEDs and sensors are also common applications for silicone.
2.3 Silicone Pressure Sensitive Adhesives
Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive is composed of high molecular weight Methyl Vinyl Polysiloxane and silicone resin, and a certain amount of solvent is for dilution. In the use of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive, generally add peroxide or Pt catalyst, crosslinking agent vulcanization after use, but also in some occasions when not vulcanized.
XJY-301 Silicone Pressure-sensitive Adhesive (PSA) is a specific structure of silicone resin and high molecular weight polydimethylsiloxane complex, it is an adhesive applied to specific scenarios under the conditions of the adhesive, has a high-temperature resistance, high stability, good electrical insulation, good transparency, high strength elastic bonds on human body, and other characteristics, have a wide range of applications in the medical and other fields.
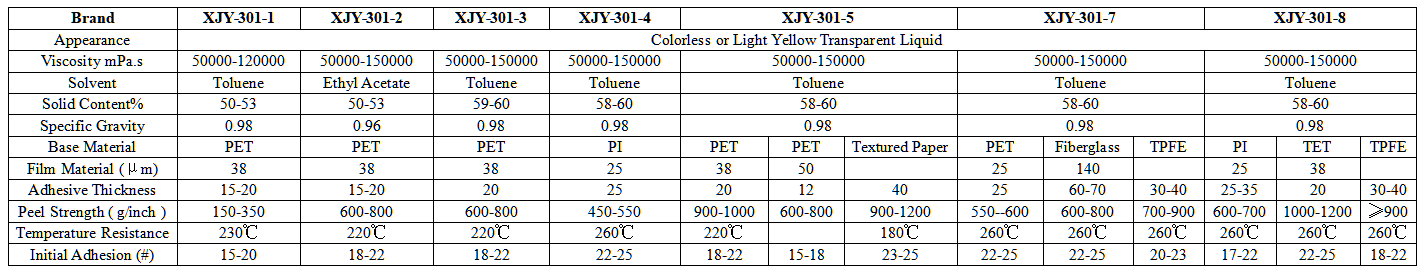
2.4 Silicone elastomer
Silicone elastomers are the most widely used silicone materials in the medical field and can be broadly divided into high-temperature compounded rubber (HCE), liquid silicone rubber (LSR), and room-temperature vulcanized silicone rubber (RTV). Among them, high-temperature compounded rubber is made of high molecular weight methyl vinyl polysiloxane, reinforcing fillers, and processing aids. It is in the form of playdough before vulcanization, and after adding a vulcanizing agent, it undergoes a cross-linking reaction under heating conditions to form an elastomer with a three-dimensional network structure.
What are the differences between silicone elastomer and silicone gel?
The composition of silicone elastomers is similar to that of gels, but due to the high content of reinforcing fillers and longer polymer chains and shows higher physical and mechanical properties. For example, elastomers have a higher viscosity than gels and liquids.
What are the differences between HCR, LCE and LSR?
HCR, LCE, and LSR are moldable materials that can be cast or injected into molds of various configurations.
High-consistency rubber (HCR) is ideal for extruded tubing because its silica-reinforced, high molecular weight polymers allow it to retain its shape while uncured;
In contrast, low-consistency elastomers (LCE) are flowable and better suited for coatings, sealants, and molded parts that require optical clarity. LCE's high clarity and low viscosity compared to HCR and liquid silicone rubber (LSR) is primarily due to its unique base formulation, which may contain phenyl.
LSR has a medium viscosity and is used to mold high-precision parts such as gaskets, valves, o-rings, and seals.
2.5 Silicone Adhesives
Low-viscosity elastomer systems containing silicone adhesive promoters are used as adhesives. They are typically dispersed in solvent systems for spray or dip applications, which require a thin protective barrier against the surrounding environment.
For example, silicones act as protective barriers in wound care dressings, external prosthetic devices, and contact lenses. Typically in these applications, the silicone also needs to be permeable to act as a membrane through which water can be transported to the surrounding tissue. On the other hand, pacemakers, cochlear implants, or other devices that rely on electronics or batteries require silicone with significantly reduced moisture permeability to avoid corrosion and delamination.
3. How to apply silicone in medical devices?
3.1 Breast augmentation materials
Medical-grade silicones can be used as implant materials in breast augmentation surgery. Compared with traditional breast augmentation materials such as saline, silicone materials are more stable, will not leak out, will not be absorbed, and at the same time will not affect the human body and skin contact, has good breast forms.
3.2 Medical piping
Silicone materials can be used for medical piping, such as catheters and infusion tubes. The excellent properties of silicone materials make it possible to meet the requirements for use in all aspects, from flow to pressure. Silicone materials are also able to withstand repeated bending and twisting without excessive wear and tear and are therefore suitable for the production of medical piping.
![]()
3.3 Eyeglasses
Silicone materials can also be used to manufacture contact lenses. Compared with traditional hard contact lenses, silicone materials are more biocompatible, do not harm the eye, and fit the eye better, thus reducing discomfort.
3.4 Artificial Joints
Silicone materials can be used in the manufacture of artificial joints, such as artificial joints and artificial knee joints. Silicone materials are stable, will not be dissolved or decomposed, in the body can also withstand repeated activities and loads, but also have good biocompatibility and will not produce adverse reactions to the human body.
3.5 Cardiac stents
Silicone materials can also be used to manufacture cardiac stents. Compared with traditional stainless steel stents and alloy stents, silicone materials are softer and can fit more closely to the cardiovascular wall, and also have excellent biocompatibility and molding properties, so they are suitable for cardiac stent production.
![]()
XJY-8206 Methyl vinyl MQ Silicone Resin is a solid powder resin, that can be used as reinforcing filler for additive molding silicone rubber, and also can be used as the basic silicone filler raw material for dental use with high transparency and high hardness.
XJY-8206N Methyl Vinyl MQ Silicone Resin + Vinyl Polydimethylsiloxane is a colorless and transparent liquid resin composed of vinyl MQ organic silicone resin and vinyl silicone oil. It can be used in LSR liquid silicone rubber and other additives and also has good reinforcing and hardening properties, widely used in the medical field.
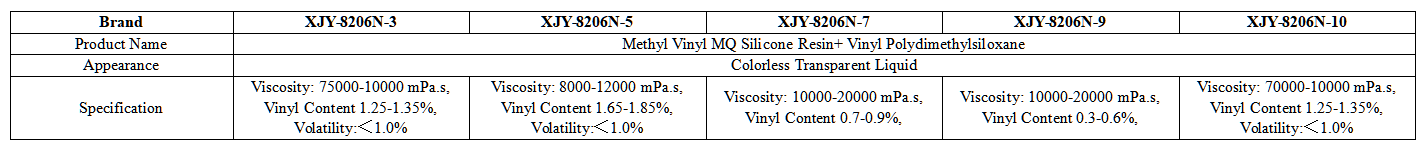
4. How to make your medical silicone performance better?
Silicone materials are soft and skin-friendly, high and low temperature resistant, radiation resistant, non-toxic and odorless, as well as biocompatible and environmentally stable, etc., and have a broad range of applications in automobiles, aircraft, military technology, and electronic equipment, etc., and are also widely used in biomedical fields, including simulation of medical models, medical implants, prosthetic limbs, embedded sensors, flexible electronics, flexible robots and so on. How to improve the competitiveness of your products?
XJY Silicones is one of the leading silicone MQ resin and VMQ silicone manufacturers in China, with more than 30 years of R&D and manufacturing experience in the silicone industry as well as more than 15 related patents and technical support. Our silicone resins can meet the needs of the medical industry and support the provision of diversified customized solutions.


